Indian will set up a satellite tracking and imaging centre in southern Vietnam by taking forward the strategic relationship between the two countries to the next level.
What is the use of this satellite for Vietnam?
It will give Vietnam an access to pictures from Indian earth observation satellites that cover the region, including China and the South China Sea.
Impact of this move:
The move could heighten tensions between the two countries(India , vietnam) and China. Both states have long-running territorial disputes with China.
The facility will be equipped to receive images from India’s Earth observation satellites that Vietnam can use in return for granting India the tracking site.
Earth observation satellites have agricultural, scientific and environmental applications, but can also provide military intelligence.
on the other side:
India extended a $100m credit line for Vietnam to buy patrol boats and is training Vietnamese submariners in India.
Vietnam has granted oil exploration blocks to India in waters off Vietnam that are disputed with China.
ONGC, the Indian company, was invited by Vietnam to do drilling in Vietnam coastal waters, block 128 of Phu Khanh Basin.
China -Vietnam dispute:
China and Vietnam fought a prolonged border war from 1979 to 1990, but have since worked to improve their diplomatic and economic ties.
The two countries remain in dispute over territorial issues in the South China Sea.
A 2014 survey conducted by the Pew Research Center showed 84% of Vietnamese were concerned that territorial disputes between China and neighbouring countries could lead to a military conflict.
Paracel island dispute Between China – Vietnam:
The Paracel Islands is a group of islands, reefs, banks and other maritime features in the South China Sea. It is controlled (and occupied) by the People’s Republic of China, and also claimed by Taiwan (Republic of China) and Vietnam.
The archipelago is approximately equidistant from the coastlines of China (PRC) and Vietnam; and approximately about one-third of the way from central Vietnam to the northern Philippines.
Disputed areas:
After Sino-French war(1884-1885), France recognized the Paracel’s and Spratly’s islands as Chinese territories, in exchange for Chinese recognition of Vietnam as a French territory.
Chinese maps since then have consistently shown China’s claims.
China in 1949, occupied Woody Island, the main island of the Amphitrite group and the only island that was occupied at the time.
Pattle Island in the Crescent group, on the other hand, was later taken by Vietnam and then controlled by South Vietnam following independence in 1956.
Tensions over the islands have continued to rise unceasingly since then.
After the military engagement(1974) and the subsequent victory, the PRC gained the entire archipelago and has taken control of Paracel Islands ever since.
It was a significant turning point for the PRC but the sovereignty dispute on the islands remains unresolved with Vietnam.
But,most of the Paracel Islands are within China’s 200 nautical-mile EEZ as defined by UNCLOS.

India – China dispute :
Sovereignty over two large and various smaller separated pieces of territory have been contested between China and India.
The westernmost, Aksai Chin, is claimed by India as part of the state of Jammu and Kashmir and region of Ladakh but is controlled and administered as part of the Chinese autonomous region of Xinjiang.It is a virtually uninhabited high altitude wasteland crossed by the Xinjiang-Tibet Highway.
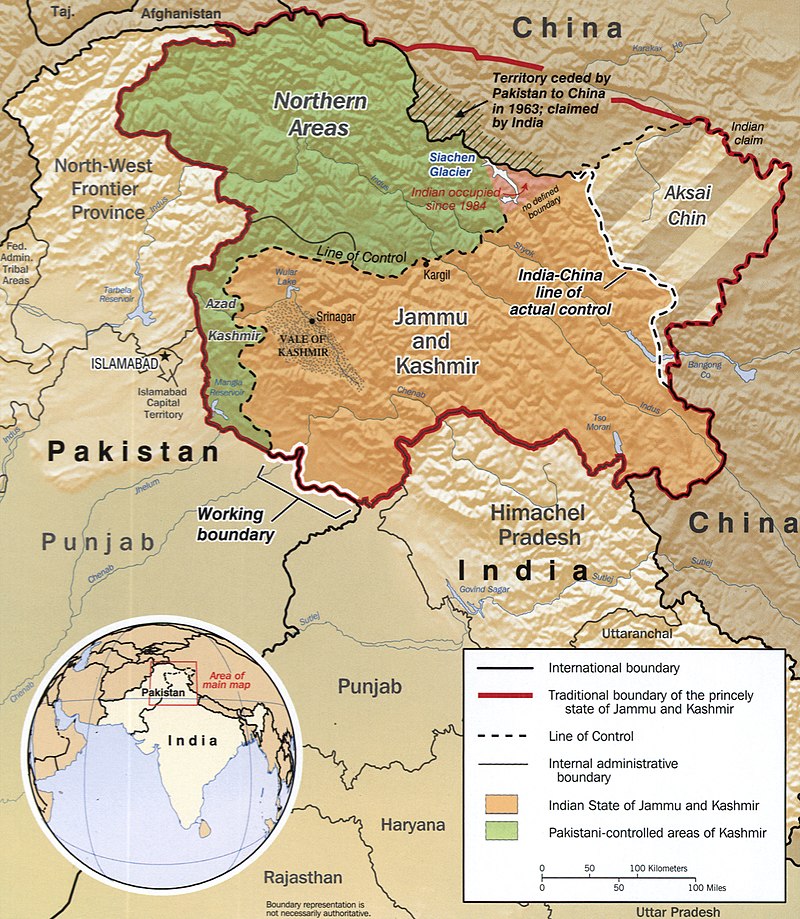
The easternmost, lies south of the McMahon Line. It was formerly referred to as the North East Frontier Agency, and is now called Arunachal Pradesh. The McMahon Line was part of the 1914 Simla Convention between British India and Tibet, an agreement rejected by China.
Comments
Post a Comment